free fall equation for time
In general relativity free fall is defined as the movement of a body along a geodesic with gravity described as space-time curvature. The value for g on Earth is 98 mss.
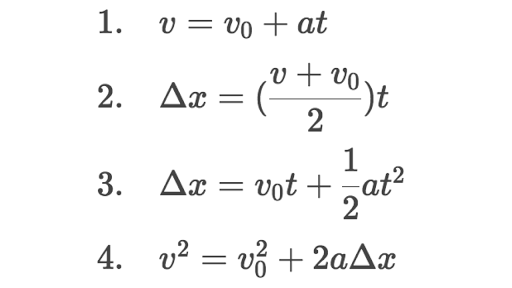
What Are The Kinematic Formulas Article Khan Academy
Today an experimental setup similar to that of Thomas Youngs is commonly used in a Physics classroom to repeat the experiment.
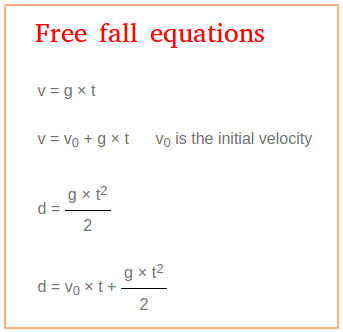
. In Newtonian physics free fall is any motion of a body where gravity is the only force acting upon it. Time t 7s We all are acquainted with the fact that free fall is independent of mass. Which is moving with higher velocity.
Also particles in the air collide with the falling object which results in transforming some of its kinetic energy into thermal energy. In 1801 this experiment was performed for the first time by Thomas Young. Access the answers to hundreds of Free fall questions that are explained in a way thats easy for you to understand.
We consider the general motion of a body about its center of mass first examining this in a inertial reference frame. Get help with your Free fall homework. Allow the body to execute free motions possibly under the action of external moments.
Fall 2009 Version 30 Lecture L28 - 3D Rigid Body Dynamics. Free Fall Equation If an object is falling toward the surface of a planet and the force of gravity is much greater than the force of air resistance or else its velocity is much less than terminal velocity the vertical velocity of free fall may be. This results in less motion or a more slowly increasing downward.
In the context of general relativity where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature a body in free fall has no force acting on it. The above equation can be used to calculate the velocity of the object after any given amount of time when dropped from rest. It does not depend on the magnitude of.
Young expanded the mathematical model presented above by relating the wavelength of light to observable and measurable distances. Example calculations for the velocity of a free-falling object after six and eight seconds are shown below. But in the real world the Earths atmosphere provides some resistance to an object in free fall.
Hence it is given as h frac12gt2 h 05 98 7 2. The gravitational acceleration vector depends only on how massive the field source is and on the distance r to the sample mass. Free-fall physics problems are having the assumption of the absence of air resistance.
In terms of time t in seconds since the object was dropped another equation for velocity is. The Velocity in free fall is autonomous of mass. The cotton falls after 3 s and iron falls after 5 s.
An object in the technical sense of the term free fall may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. Free Fall Questions and Answers. It is a vector oriented toward the field source of magnitude measured in acceleration units.
Here is the frictionless free-fall acceleration sustained by the sampling mass under the attraction of the gravitational source. Derivation of Youngs Equation. V gt 981 x 10 981 ms or 355 kmhr 219 miles per hour However as we shall see drag puts an upper limit on velocity.
At an instant of time we can calculate the angular momentum of the body as H. To put this into perspective after 10 seconds of free fall in a vacuum an object would be traveling at. H 2401 m.
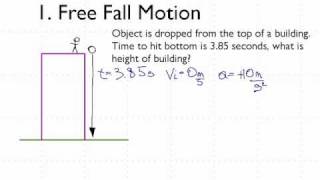
Free Falling Objects Boundless Physics
Kinematic Equations And Problem Solving

Free Fall Motion Kinematic Equations For Free Fall

Different Equations Of Motion For Free Falling Object Teachoo
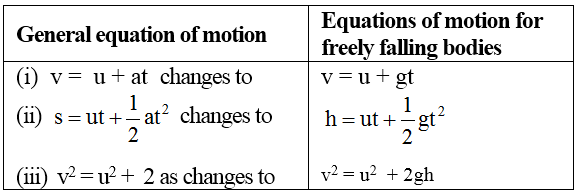
Equations Of Motion For Freely Falling Object A Plus Topper

Free Fall Motion Kinematic Equations For Free Fall

Free Fall Distance And Velocity Calculator High Accuracy Calculation
